Data configuration¶
Inside the experiment configuration file, you need to specify the configuration for loading and splitting the dataset. This part of the configuration can be a bit tricky to understand at first, so we will try to explain it in more detail here.
Let’s start by looking at the dataset configuration:
data:
dataset:
name: mnist # Dataset's name
params: ...
distribution:
name: iid # IID/non-IID data distribution
params: ...
sampling_perc: 1 # Sampling percentage when loading the dataset.
keep_test: true # Whether to keep the test set as provided by the dataset.
client_split: 0 # Client-side test set split percentage.
server_test: true # Whether the server has a test set
server_split: 0.0 # The size of the server split
uniform_test: false # Whether to use client-side a iid test set distribution regardless
Now let’s dive into each of these fields.
Dataset configuration¶
The first field is the dataset field. Here you specify the name of the dataset you want to use.
Currently, in fluke the following datasets are supported: mnist, svhn, mnistm, femnist, emnist, cifar10, cifar100, tiny_imagenet, shakespeare, fashion_mnist, cinic10.
The params field is a placeholder that represents the potential parameter(s) for loading the dataset correctly.
For example, let’s say you want to load the mnist dataset and you already downloaded (or you want to download) it to a specific folder called mnist_data.
You can specify the path to the folder with the parameter path:
data:
dataset:
name: mnist
path: mnist_data
...
Tip
If you want to get more details about the datasets and their possible parametrization, please have a look at the API documentation of fluke.data.datasets.
If no parameters are needed, you can simply remove the params field.
You are not obliged to only use the datasets provided by fluke. You can also use your own dataset by creating a
new dataset function as described in this tutorial.
Data distribution¶
The distribution field is where you specify the data distribution you want to use.
The name field is where you specify the name of the data distribution you want to use, and
the params field is a placeholder that represents the potential parameter(s) of the distribution.
Currently, in fluke the following data distributions are supported:
iid: classic IID data distribution; No parameters required.qnt: Quantity skewed data. Distribute the examples across the clients according to the following probability density function: \(P(x; \alpha) = \alpha x^{\alpha-1}\) where \(x\) is the id of a client (\(x \in [0, n-1]\)), and \(\alpha > 0\). You can specify the parameteralpha(default is 4) and themin_quantity(default is 2) parameter that represents the minimum number of examples per client.lbl_qnt: Label quantity skewed data. This is still a class-wiese quantity skewed data distribution, but the skeweness is achieved in a different way. Suppose each party only has data samples ofclass_per_client(a required parameter, by default 2) different labels. We first randomly assignclass_per_clientdifferent label IDs to each party. Then, for the samples of each label, we randomly and equally divide them into the parties which own such label. In this way, the number of labels in each party is fixed, and there is no overlap between the samples of different parties.dir: Label skewed data according to the Dirichlet distribution. The parameterbetais required (default is 0.1). You can also set the minimum number of examples per class (min_ex_class, default is 2).pathological: Pathological skewed data. Each client has data from few classes. The method first sort the data by label, divide it inton * shards_per_clientshards, and assign each ofnclientsshards_per_clientshards.shards_per_clientis a required parameter (default is 2).
Other fields¶
Besides the dataset and distribution fields, there are other fields that you need to specify. These fields are related to the way the dataset is split between the clients and the server.
Sampling percentage¶
The sampling_perc field is used when you want to use only part of the dataset. This is meant to be used for debugging purposes.
It represents the sampling percentage when loading the dataset.
If set to a value that is less than one, than at each iteration over the client’s FastDataLoader
the dataset will be sampled with the given percentage. Note that the sampling is repeated each time, so the sample of the dataset will be different at each round.
Splitting the dataset¶
The other remaining fields are related to each other and are used to specify how to split the dataset between the clients and the server.
keep_test: all the supported datasets influkecome with a test set. Thekeep_testfield is used to specify whether you want to keep the test set as provided by the dataset (see scenarios (a), (b) and (c) in the figures below). Keeping the test set means that those examples will be used for evaluation purposes (either server-side or client-side).server_test: specifies whether the server has a test set. Ifkeep_testis set totrue, then the server will have the test set provided by the dataset.client_split: specifies the percentage of the client’s data that will be used as a test set. If set to0, the clients do not have a test set, i.e., no evaluation client-side (see scenarios (a) and (d) in the figures below).server_split: this field is only used whenkeep_testis set tofalseandserver_testis set totrue. It specifies the size of the server split w.r.t. the entire dataset (see scenarios (d) and (e) in the figures below).uniform_test: specifies whether to use a client-side IID test set distribution regardless of the training data distribution. If set tofalse, the test set will be split according to the indicated data distribution. Note: currently, ifkeep_test=trueandserver_test=falsethe dataset’s test is always uniformly distributed across clients. Thus, this field is ignored in that case.
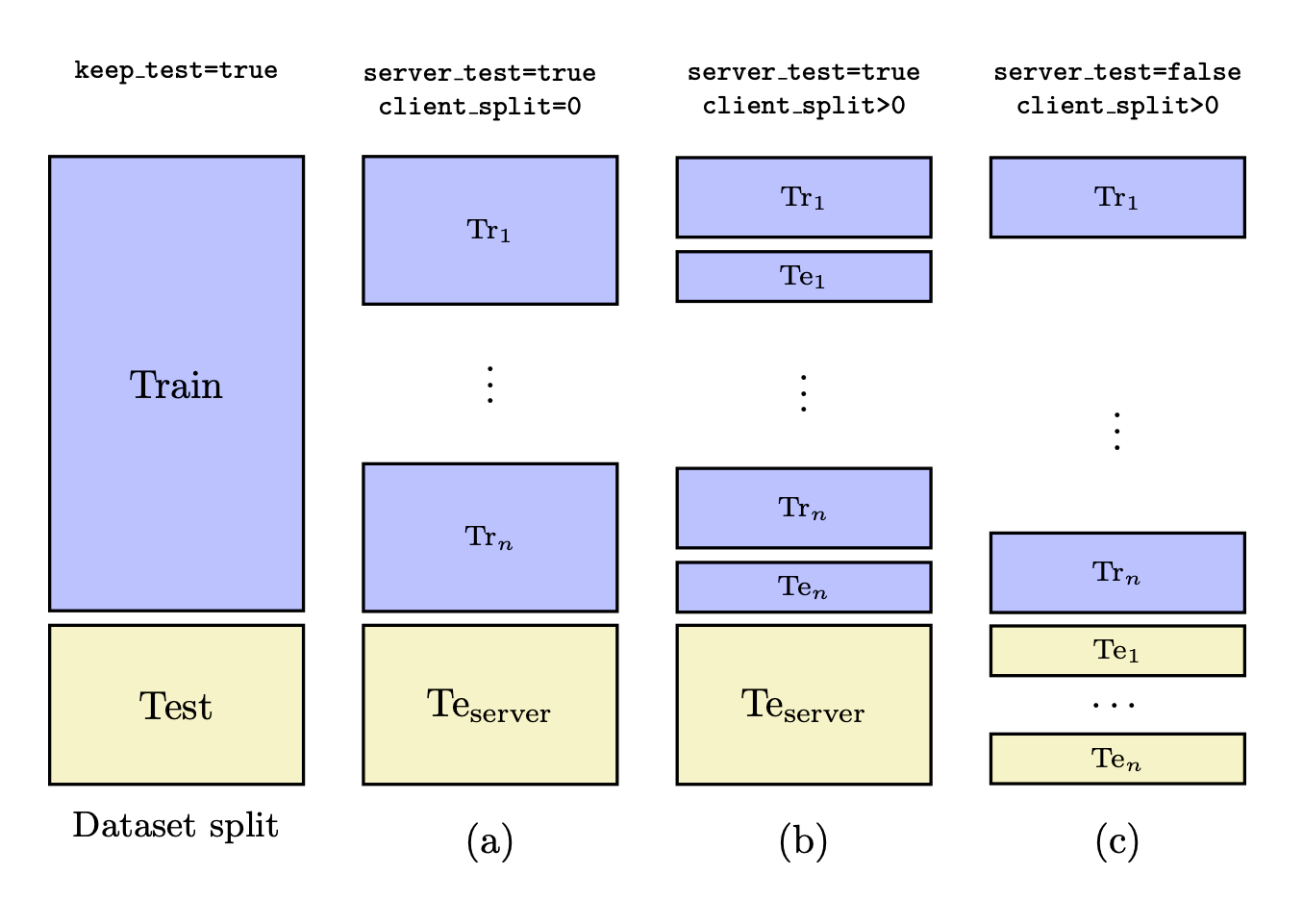
Dataset splitting scenarios when keep_test is set to True.
This image has been created with TikZ [source].¶
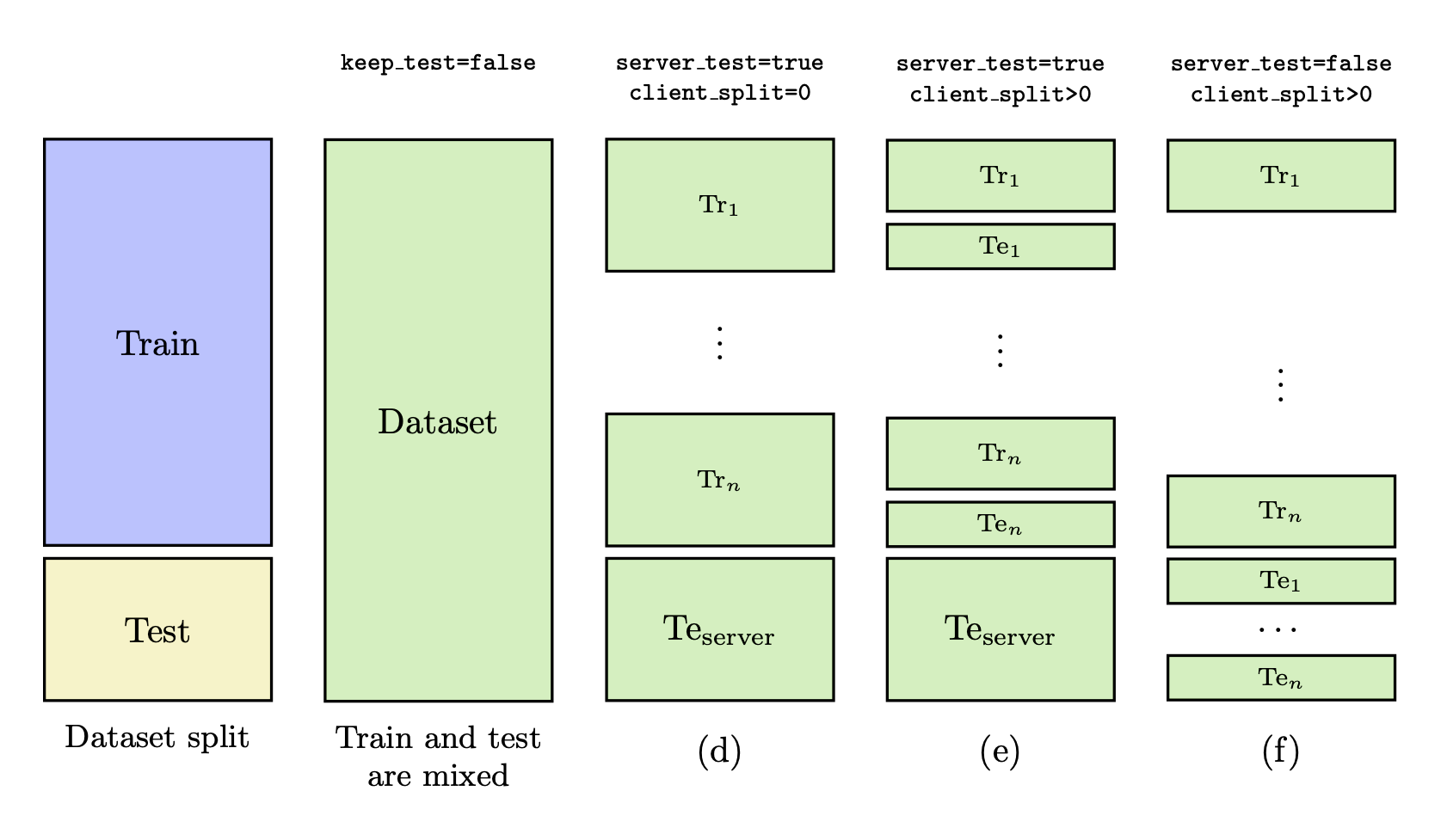
Dataset splitting scenarios when keep_test is set to False.
This image has been created with TikZ [source].¶